Stacks blockchain API
The Stacks 2.0 blockchain API allows you to query the Stacks 2.0 blockchain and interact with smart contracts. It was built to maintain paginated, materialized views of the Stacks 2.0 Blockchain.
This API is hosted by Hiro. Using it requires you to trust the hosted server, but provides a faster development experience. Consider running your own API instance to create a fully trustless architecture for your app.
The RESTful JSON API can be used without any authorization. The base path for the API is:
# for mainnet, replace `testnet` with `mainnet`
https://stacks-node-api.testnet.stacks.co/
Review the Stacks API reference for more details
The API is comprised of two parts: the Stacks Blockchain API and the Stacks Node RPC API. The Node RPC API is exposed by every running node. Stacks Blockchain API, however, introduces additional capabilities (for example, retrieving all transactions). It also proxies calls directly to Stacks Node RPC API.
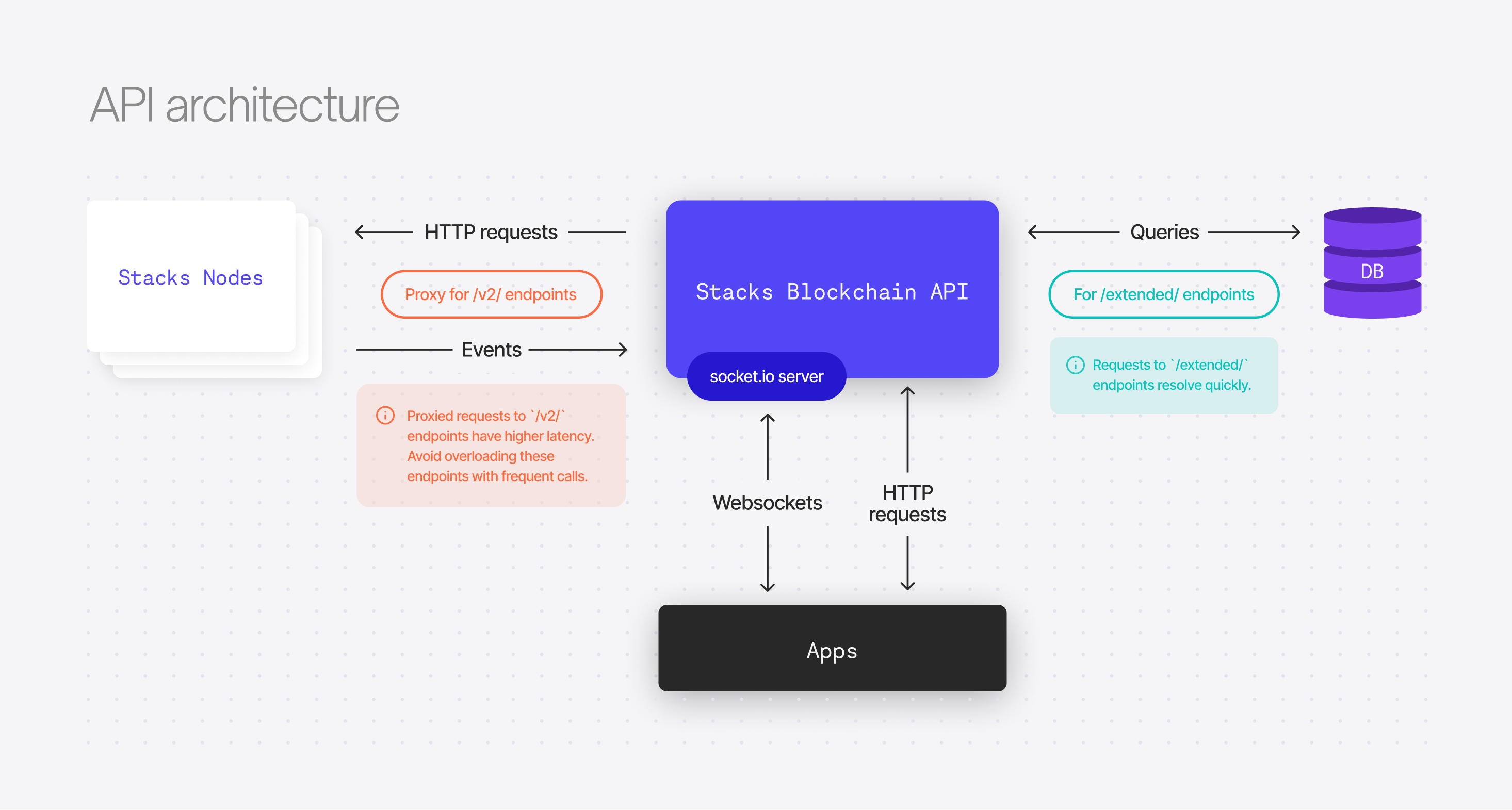
Stacks node RPC API
The stacks-node implementation exposes JSON RPC endpoints.
All /v2/ routes are routed through a proxy to a Hiro-hosted Stacks Node. For a trustless architecture, you should make these requests to a self-hosted node.
Stacks blockchain API
All /extended/ routes are provided by the Stacks 2.0 Blockchain API directly. They extend the Stacks Node API capabilities to make it easier to integrate with.
Using the API
Depending on your development environment, you can access the API through a variety of methods. The easiest way to start interacting with the API is through the Postman Collection or cURL.
Postman allows you to generate sample code for API requests for various languages and libraries.
OpenAPI spec
The Stacks API was designed using the OpenAPI specification, making it compatible with a variety of developer tools.
The OpenAPI specification file for Stacks is used to generate the TypeScript client library. You can use the specification file to generate client libraries for other programming languages using the openapi-generator tool
TypeScript client library
A Typescript client library is available for use of the Stacks API. The client library enables type-safe REST and WebSocket communication with the Stacks API endpoints. Review the client documentation for more details.
The client is made up of three components:
- Generated HTTP API client
- Typescript definitions for Clarity values
- WebSocket client
The following sections demonstrate common usages of the TypeScript API client.
HTTP API client sample
The Typescript client library requires you to specify the underlying HTTP request library to handle HTTP communication. The example below uses the universal fetch API cross-fetch:
import fetch from 'cross-fetch';
import { Configuration, AccountsApi } from '@stacks/blockchain-api-client';
(async () => {
const apiConfig = new Configuration({
fetchApi: fetch,
// for mainnet, replace `testnet` with `mainnet`
basePath: 'https://stacks-node-api.testnet.stacks.co', // defaults to http://localhost:3999
});
// initiate the /accounts API with the basepath and fetch library
const accountsApi = new AccountsApi(apiConfig);
// get transactions for a specific account
const txs = await accountsApi.getAccountTransactions({
principal: 'ST000000000000000000002AMW42H',
});
console.log(txs);
})().catch(console.error);
TypeScript sample
The following sample demonstrate how generated TypeScript models can be used for type-safety:
import fetch from 'cross-fetch';
import {
Configuration,
AccountsApi,
AccountsApiInterface,
AddressBalanceResponse,
AddressBalanceResponseStx,
} from '@stacks/blockchain-api-client';
(async () => {
const apiConfig: Configuration = new Configuration({
fetchApi: fetch,
// for mainnet, replace `testnet` with `mainnet`
basePath: 'https://stacks-node-api.testnet.stacks.co', // defaults to http://localhost:3999
});
const principal: string = 'ST000000000000000000002AMW42H';
// initiate the /accounts API with the basepath and fetch library
const accountsApi: AccountsApiInterface = new AccountsApi(apiConfig);
// get balance for a specific account
const balance: AddressBalanceResponse = await accountsApi.getAccountBalance({
principal,
});
// get STX balance details
const stxAmount: AddressBalanceResponseStx = balance.stx;
console.log(stxAmount);
})().catch(console.error);
WebSocket sample
The WebSocket components enabled you to subscribe to specific updates, enabling a near real-time display of updates on transactions and accounts.
import { connectWebSocketClient } from '@stacks/blockchain-api-client';
const client = await connectWebSocketClient('ws://stacks-node-api.blockstack.org/');
const sub = await client.subscribeAddressTransactions(contractCall.txId, event => {
console.log(event);
});
await sub.unsubscribe();
Rate limiting
Rate limiting is only applied to faucet requests based on the requested token addresses.
You can refer to the rate limit for each endpoint in the table below:
| Endpoint | Rate-Limit (RPM) |
|---|---|
| stacks-node-api.mainnet.stacks.co/extended/ stacks-node-api.stacks.co/extended/ | 500 |
| stacks-node-api.mainnet.stacks.co/rosetta/ stacks-node-api.stacks.co/rosetta/ | 200 |
| stacks-node-api.mainnet.stacks.co/v2/ stacks-node-api.stacks.co/v2/ | 100 |
| stacks-node-api.testnet.stacks.co/extended/ | 100 |
| stacks-node-api.testnet.stacks.co/v2/ | 100 |
| stacks-node-api.testnet.stacks.co/extended/v1/faucets/ | 1 |
STX faucet
The Stacks faucet rate limits depend on the type of request. For stacking requests, a limitation of 1 request per 2 days. In case of regular Stacks faucet requests, the limits are set to 1 request per minute.
Pagination
To make API responses more compact, lists returned by the API are paginated. For lists, the response body includes:
limit: the number of list items return per responseoffset: the number of elements to skip (starting from 0)total: the number of all available list itemsresults: the array of list items (length of array equals the set limit)
Here is a sample response:
{
"limit": 10,
"offset": 0,
"total": 101922,
"results": [{
"tx_id": "0x924e0a688664851f5f96b437fabaec19b7542cfcaaf92a97eae43384cacd83d0",
"nonce": 308,
"fee_rate": "0",
"sender_address": "ST39F7SA0AKH7RB363W3NE2DTHD3P32ZHNX2KE7J9",
"sponsored": false,
"post_condition_mode": "deny",
"post_conditions": [],
"anchor_mode": "on_chain_only",
"block_hash": "0x17ceb3da5f36aab351d6b14f5aa77f85bb6b800b954b2f24c564579f80116d99",
"parent_block_hash": "0xe0d1e8d216a77526ae2ce40294fc77038798a179a6532bb8980d3c2183f58de6",
"block_height": 14461,
"burn_block_time": 1622875042,
"burn_block_time_iso": "2021-06-05T06:37:22.000Z",
"canonical": true,
"tx_index": 0,
"tx_status": "success",
"tx_result": { ... },
"microblock_hash": "",
"microblock_sequence": 2147483647,
"microblock_canonical": true,
"event_count": 0,
"events": [],
"tx_type": "coinbase",
"coinbase_payload": { ... }
},
{ ... }
]
}
Using the limit and offset properties, you can paginate through the entire list by increasing the offset by the limit until you reach the total.
Requesting proofs
Several endpoints will by default request the MARF Merkel Proof.
Provided with the proof, a client can verify the value, cumulative energy spent, and the number of confirmation for the response value provided by the API.
Requesting the proof requires more resources (computation time, response time, and response body size). To avoid the additional resources, in case verification is not required, API endpoints allow setting the request parameter: proof=0. The returned response object will not have any proof fields.
Searching
The API provides a search endpoint (/extended/v1/search/{id}) that takes an identifier and responds with matching blocks, transactions, contracts, or accounts.
The search operation used by the endpoint (for example, FROM txs WHERE tx_id = $1 LIMIT 1) matches hashes equal to the provided identifier. Fuzzy search, incomplete identifiers, or wildcards will not return any matches.
Using Clarity values
Some endpoints, like the read-only function contract call, require input to as serialized Clarity value. Other endpoints return serialized values that need to be deserialized.
Below is an example for Clarity value usage in combination with the API.
The example below is for illustration only. The @stacks/transactions library supports typed contract calls and makes response value utilization much simpler
import {
Configuration,
SmartContractsApiInterface,
SmartContractsApi,
ReadOnlyFunctionSuccessResponse,
} from '@stacks/blockchain-api-client';
import { uintCV, UIntCV, cvToHex, hexToCV, ClarityType } from '@stacks/transactions';
(async () => {
const apiConfig: Configuration = new Configuration({
fetchApi: fetch,
// for mainnet, replace `testnet` with `mainnet`
basePath: 'https://stacks-node-api.testnet.stacks.co', // defaults to http://localhost:3999
});
const contractsApi: SmartContractsApiInterface = new SmartContractsApi(apiConfig);
const principal: string = 'ST000000000000000000002AMW42H';
// use most recent from: https://stacks-node-api.<mainnet/testnet>.stacks.co/v2/pox
const rewardCycle: UIntCV = uintCV(22);
// call a read-only function
const fnCall: ReadOnlyFunctionSuccessResponse = await contractsApi.callReadOnlyFunction({
contractAddress: principal,
contractName: 'pox',
functionName: 'is-pox-active',
readOnlyFunctionArgs: {
sender: principal,
arguments: [cvToHex(rewardCycle)],
},
});
console.log({
status: fnCall.okay,
result: fnCall.result,
representation: hexToCV(fnCall.result).type === ClarityType.BoolTrue,
});
})().catch(console.error);
Error handling
The API can respond with two different error types:
- For URLs that don't match any defined endpoint, an HTTP 404 is returned. The body lists the URL in reference (as a string)
- For invalid input values (URL/body parameters), an HTTP 500 is returned. The body is a JSON object with an
errorproperty. The object also includes stack trace (stack) and an error UUID (errorTag)
Proxied Stacks Node RPC API endpoints
The Stacks 2.0 Blockchain API is centrally hosted. However, every running Stacks node exposes an RPC API, which allows you to interact with the underlying blockchain. Instead of using a centrally hosted API, you can directly access the RPC API of a locally hosted Node.
The Stacks Blockchain API proxies to Node RPC endpoints
While the Node RPC API doesn't give the same functionality as the hosted Stacks 2.0 Blockchain API, you get similar functionality in a way that is scoped to that specific node. The RPC API includes the following endpoints:
- POST /v2/transactions
- GET /v2/contracts/interface/{contract_address}/{contract_name}
- POST /v2/map_entry/{contract_address}/{contract_name}/{map_name}
- GET /v2/contracts/source/{contract_address}/{contract_name}
- GET /v2/accounts/{principal}
- POST /v2/contracts/call-read/{contract_address}/{contract_name}/{function_name}
- GET /v2/fees/transfer
- GET /v2/info
If you run a local node, it exposes an HTTP server on port 20443. The info endpoint would be localhost:20443/v2/info.
Rosetta support
This API supports v1.4.6 of the Rosetta specification. This industry open standard makes it simple to integrate blockchain deployment and interaction.
Find all Data and Construction Rosetta endpoints here
Microblocks support
!> API support for microblocks is a work-in-progress. Review the API documentation carefully to ensure that you are up-to-date on the latest implementation details for microblocks.
The API allows querying the most recently streamed microblocks:
# for mainnet, remove `.testnet`
curl 'https://stacks-node-api-microblocks.testnet.stacks.co/extended/v1/microblock'
{
"limit": 20,
"offset": 0,
"total": 8766,
"results": [
{
"canonical": true,
"microblock_canonical": true,
"microblock_hash": "0xe6897aab881208185e3fb6ba58d9d9e35c43c68f13fbb892b20cebd39ac69567",
"microblock_sequence": 0,
"microblock_parent_hash": "0xe0d1e8d216a77526ae2ce40294fc77038798a179a6532bb8980d3c2183f58de6",
"parent_index_block_hash": "0x178cd9a37bf38f6b85d9f18e65588e60782753b1463ae080fb9865938b0898ea",
"block_height": 14461,
"parent_block_height": 14460,
"parent_block_hash": "0xe0d1e8d216a77526ae2ce40294fc77038798a179a6532bb8980d3c2183f58de6",
"block_hash": "0x17ceb3da5f36aab351d6b14f5aa77f85bb6b800b954b2f24c564579f80116d99",
"txs": ["0x0622e096dec7e2f6e8f7d95f732e04d238b7381aea8d0aecffae026c53e73e05"]
}
]
}
Nonce handling
In order to prevent stuck transactions, you must track the next available nonce for principals issuing transactions. The API provides an endpoint to make nonce handling simpler:
# for mainnet, remove `.testnet`
# replace <principal> with your STX address
curl 'https://stacks-node-api-microblocks.testnet.stacks.co/extended/v1/address/<principal>/nonces'
{
"last_executed_tx_nonce": 5893,
"last_mempool_tx_nonce": null,
"possible_next_nonce": 5894,
"detected_missing_nonces": []
}
You can use the possible_next_nonce property as the nonce for your next transaction.
Running an API server
While Hiro provides a hosted API server of the Stacks Blockchain API, anyone can spin up their own version. Please follow the instructions in this guide to start a Docker container with the API service running.
Once started, the API is available on localhost:3999